Lung transplant surgery
Find out what happens during the transplant operation
Key points
- You will be put to sleep under a general anaesthetic while the transplant takes place
- The surgery will take 6-8 hours
- Your own lung or lungs are removed and the donor lung or lungs are put into your chest
- The operation can be performed a variety of ways, which will depend on your needs and the preference of the transplant surgeon
How is lung transplant surgery performed?
Donor lungs are transplanted in the same place as your own lungs. This involves the removal of the diseased lung and replacement with the donor lung. There are different ways that a lung can be transplanted. The surgical team caring for you will explain their preferred technique, and which would be best for you.
How it works
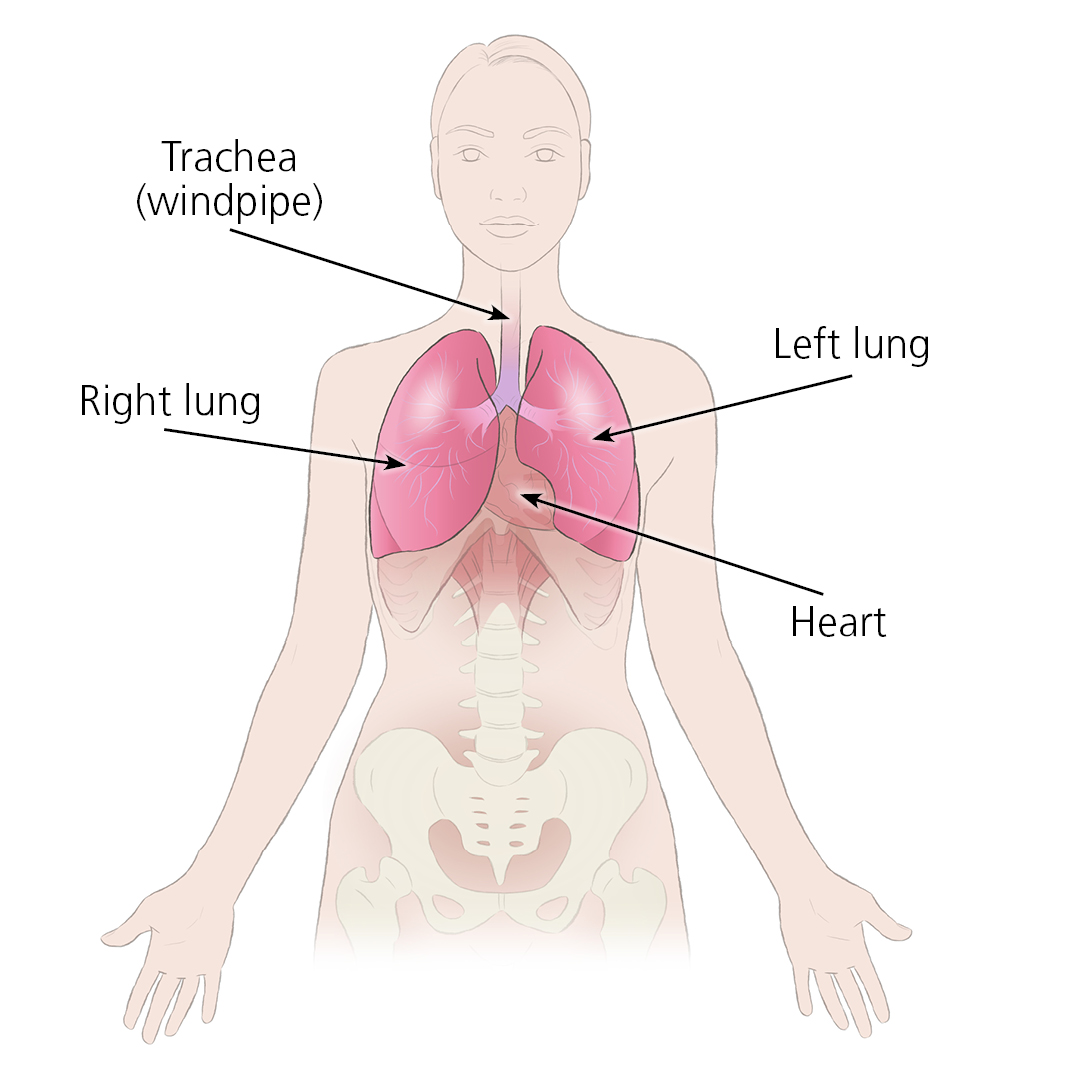
Where lungs are in the body
You have a right and left lung, these are connected to your trachea (windpipe) via the right and left bronchi. When you breathe, air goes down the trachea into your lungs. Your heart sits between the right and left lungs, with a slight tilt towards the left.
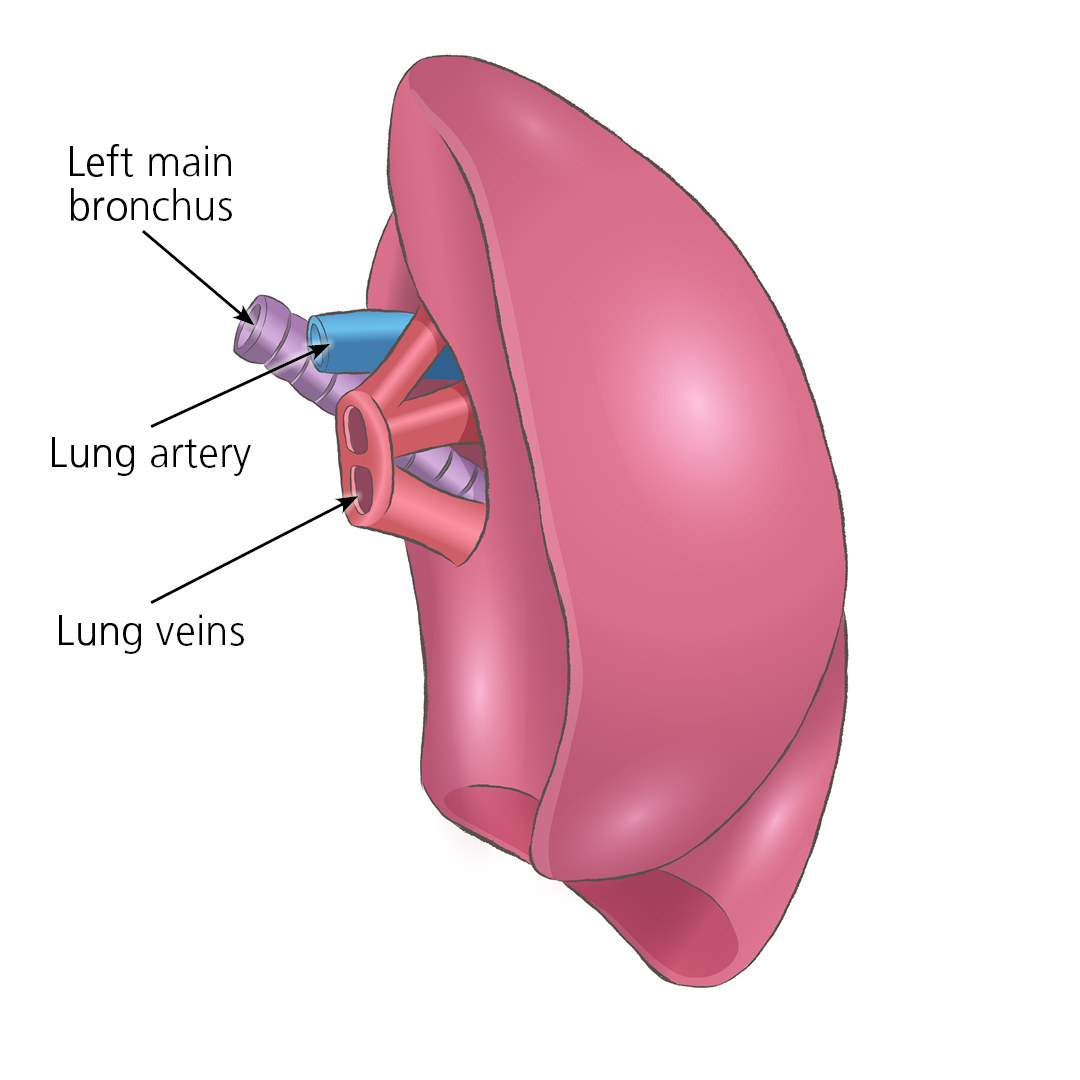
Close up of a lung
This is a close up of a left lung. The lung artery (blue) takes blood from the heart to the lungs. The lung veins (red) take oxygenated blood away from the lungs. The left main bronchus (purple) attaches to your trachea (windpipe) and brings air into your lungs.
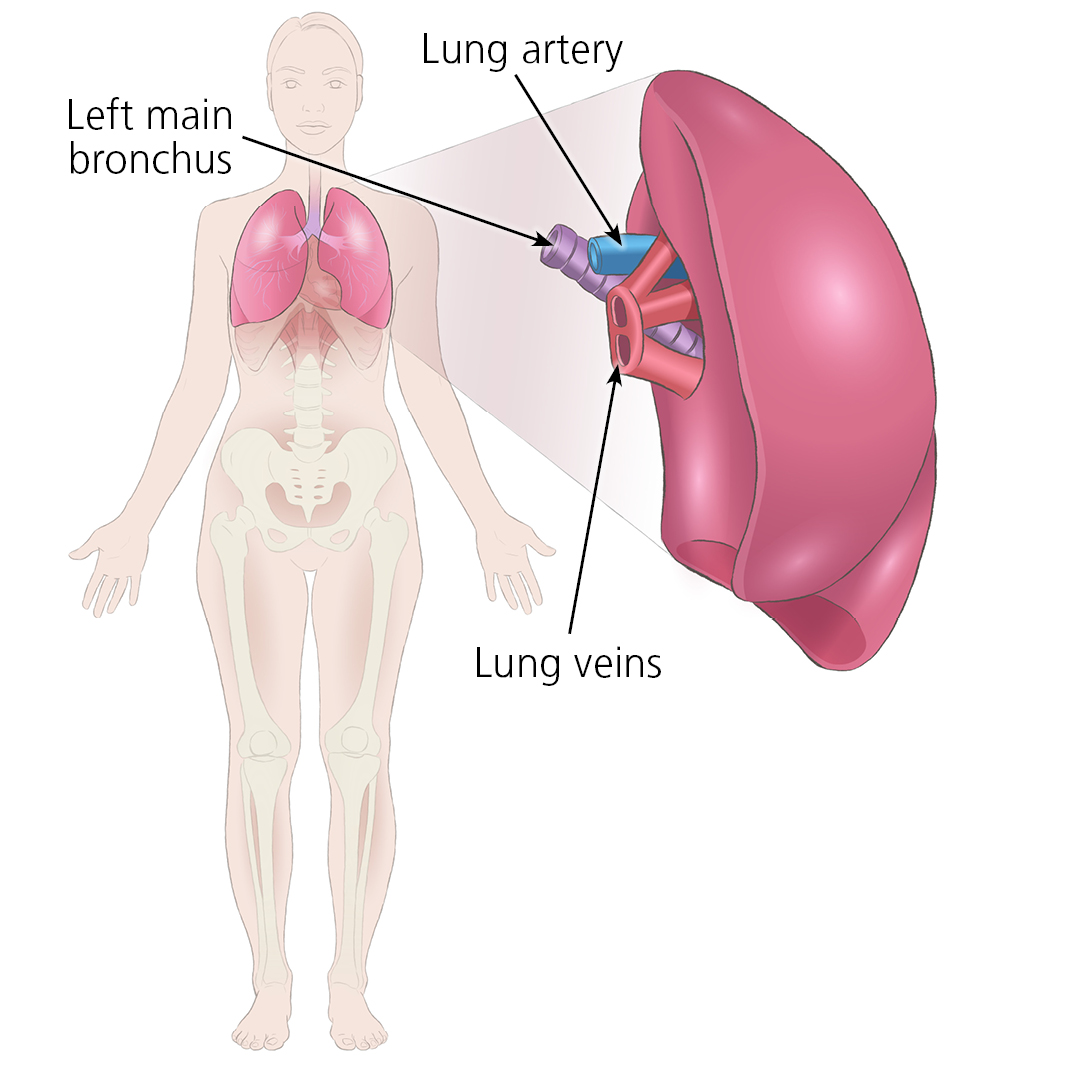
Connecting a donor lung
A donor lung is transplanted in the same place as your diseased lung. It is connected at these 3 points - the main bronchus (purple), lung artery (blue) and lung veins (red).
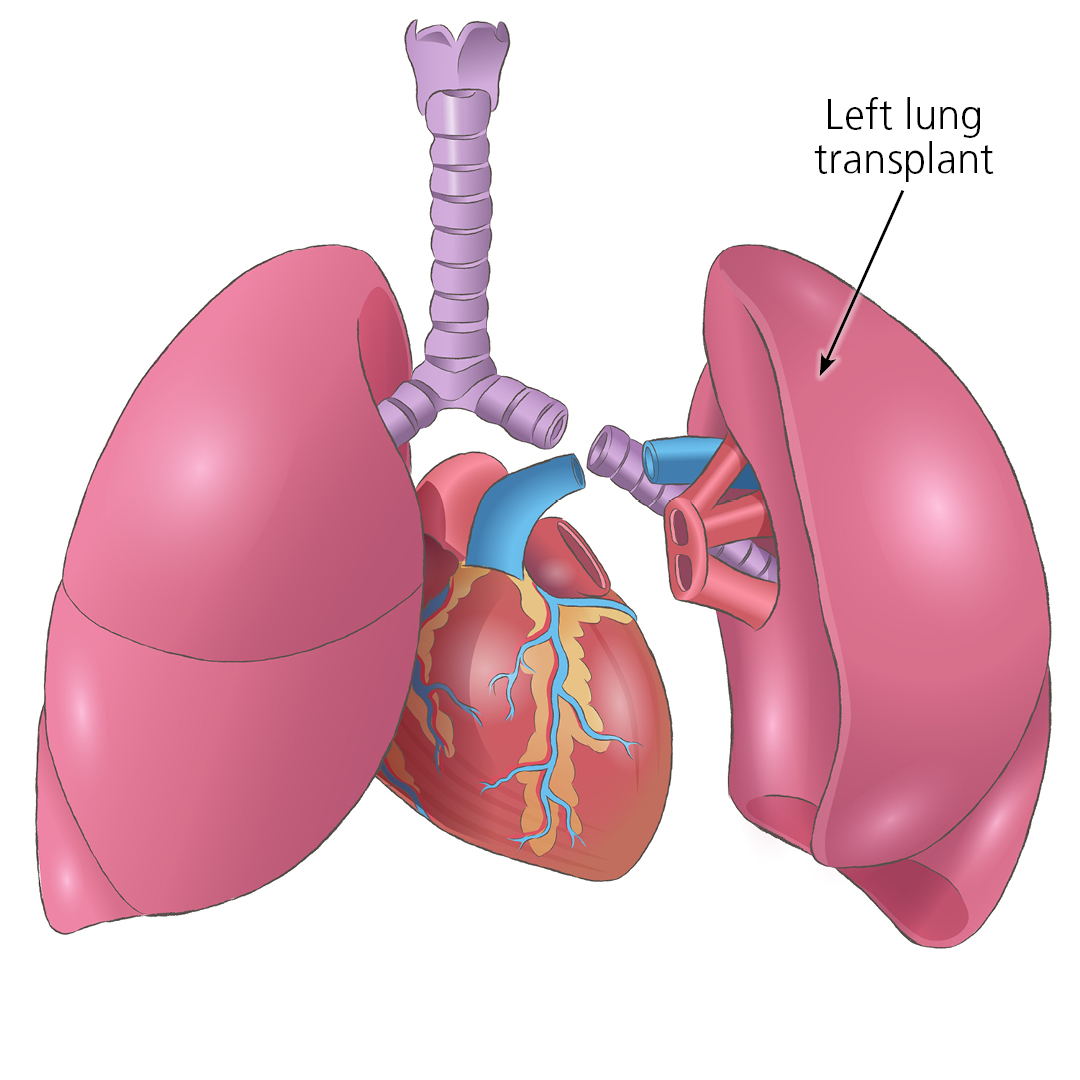
Close up of a left lung transplant
This shows how a left lung transplant connects to your trachea (windpipe) and heart. The purple tube on the transplanted lung is the left main bronchus, which connects to the trachea (windpipe). The blue artery and red veins on the left lung transplant connect to the heart.
Some things that might happen during your lung transplant surgery
Example of a surgical lung transplant technique
After you have been put to sleep under anaesthetic, the surgery will begin.
The removal of your diseased lung requires careful dissection from your heart and chest wall.
The donor lung is stitched into exactly the same place as your own lung.
More information
Related content
Medical terms explained
Biopsy
This is when a very small piece of tissue is taken for analysis. It is used to diagnose rejection.


